Lysergamides
Appearance
(Redirected from Lysergamide)
Amides of lysergic acid are collectively known as lysergamides or ergoamides,[1] and include a number of compounds with potent agonist and/or antagonist activity at various serotonin and dopamine receptors. Lysergamides contain an embedded tryptamine structure, and as a result can produce similar, often psychedelic, effects to those of the true tryptamines. [2][3][4][5][6][7][8][9][10][11][12][13][14][15][16]

| Structure | Name | CAS number | R1 | R6 | R2 | R3 | Other |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
LSA / LAA | 478-94-4 | H | CH3 | H | H | - |
 |
DAM-57 | 4238-84-0 | H | CH3 | CH3 | CH3 | - |
 |
Ergometrine (Ergonovine) | 60-79-7 | H | CH3 | CH(CH3)CH2OH | H | - |
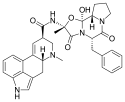 |
Ergotamine | 113-15-5 | H | CH3 | -- | C17H18N2O4 | - |
 |
Methergine | 113-42-8 | H | CH3 | CH(CH2CH3)CH2OH | H | - |
 |
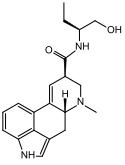
Methysergide | 361-37-5 | CH3 | CH3 | CH(CH2CH3)CH2OH | H | - |
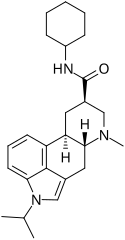 |
Amesergide | 121588-75-8 | CH(CH3)2 | CH3 | C6H11 | H | - |
 |
LY-215840 | 137328-52-0 | CH(CH3)2 | CH3 | C5H8OH | H | - |
 |
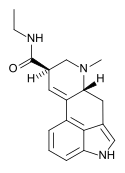
Cabergoline | 81409-90-7 | H | H2C=CH-CH2 | CONHCH2CH3 | CH2CH2CH2N(CH3)2 | - |
 |
LAE-32 | 478-99-9 | H | CH3 | CH2CH3 | H | - |
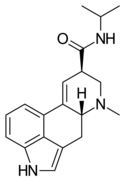 |
LAiP | H | CH3 | CH(CH3)2 | H | - | |
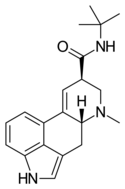 |
LAtB | H | CH3 | C(CH3)3 | H | - | |
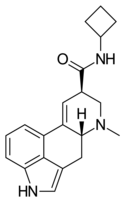 |
LAcB | H | CH3 | (CH2)4 | H | - | |
 |
Cepentil | H | CH3 | (CH2)5 | H | - | |
 |
LSB | 137765-82-3 | H | CH3 | CH(CH3)CH2CH3 | H | - |
 |
LSP | H | CH3 | CH(CH2CH3)CH2CH3 | H | - | |
 |
DAL | H | CH3 | H2C=CH-CH2 | H2C=CH-CH2 | - | |
 |
MIPLA | 100768-08-9 | H | CH3 | CH(CH3)2 | CH3 | - |
 |
EIPLA | H | CH3 | CH(CH3)2 | CH2CH3 | - | |
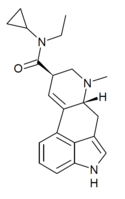 |
ECPLA | H | CH3 | C3H5 | CH2CH3 | - | |
 |
ETFELA | H | CH3 | CH2CF3 | CH2CH3 | - | |
 |
LAMPA | 40158-98-3 | H | CH3 | CH2CH2CH3 | CH3 | - |
 |
EPLA | H | CH2CH3 | CH2CH2CH3 | CH3 | - | |
 |
LSD / LAD | 50-37-3 | H | CH3 | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | - |
 |
ETH-LAD | 65527-62-0 | H | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | - |
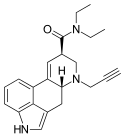 |
PARGY-LAD | H | HC≡C−CH2 | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | - | |
 |
AL-LAD | 65527-61-9 | H | H2C=CH-CH2 | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | - |
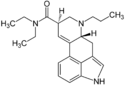 |
PRO-LAD | 65527-63-1 | H | CH2CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | - |
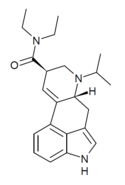 |
IP-LAD | H | CH(CH3)2 | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | - | |
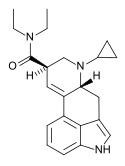 |
CYP-LAD[17] | H | C3H5 | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | - | |
 |
BU-LAD | 96930-87-9 | H | CH2CH2CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | - |
 |
FLUORETH-LAD[18] | H | CH2CH2F | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | - | |
 |
ALD-52 | 3270-02-8 | COCH3 | CH3 | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | - |
 |
1P-LSD | 2349358-81-0 | COCH2CH3 | CH3 | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | - |
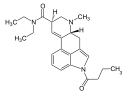 |
1B-LSD | 2349376-12-9 | COCH2CH2CH3 | CH3 | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | - |
 |
1V-LSD | CO(CH2)3CH3 | CH3 | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | - | |
 |
1H-LSD[19] | CO(CH2)4CH3 | CH3 | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | - | |
 |
1DD-LSD | CO(CH2)10CH3 | CH3 | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | - | |
 |
1cP-LSD[20] | COC3H5 | CH3 | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | - | |
 |
1D-LSD | COC4H5(CH3)2 | CH3 | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | - | |
 |
1T-LSD | COC4H3S | CH3 | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | - | |
 |
1S-LSD | CO(CH2)2Si(CH3)3 | CH3 | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | - | |
 |
1P-AL-LAD | COCH2CH3 | H2C=CH-CH2 | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | - | |
 |
1cP-AL-LAD | COC3H5 | H2C=CH-CH2 | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | - | |
 |
1T-AL-LAD[21] | COC4H3S | H2C=CH-CH2 | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | - | |
 |
1P-ETH-LAD | COCH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | - | |
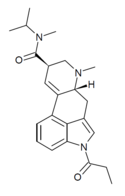 |
1P-MIPLA | COCH2CH3 | CH3 | CH(CH3)2 | CH3 | - | |
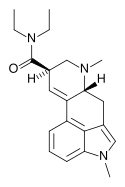 |
MLD-41 | 4238-85-1 | CH3 | CH3 | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | - |
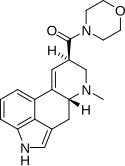 |
LSM-775 | 4314-63-0 | H | CH3 | CH2CH2-O-CH2CH2 | - | |
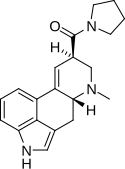 |
LPD-824 | 2385-87-7 | H | CH3 | (CH2)4 | - | |
 |
LSD-Pip | 50485-23-9 | H | CH3 | (CH2)5 | - | |
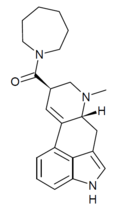 |
LSD-Azapane | H | CH3 | (CH2)6 | - | ||
 |
LA-SS-Az | 470666-31-0 | H | CH3 | CH2(CHCH3)2CH2 | - | |
 |
2-Bromo-LSD | 478-84-2 | H | CH3 | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | 2-Br |
 |
12-Methoxy-LSD[22] | 50484-99-6 | H | CH3 | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | 12-OMe |
 |
13-Fluoro-LSD[23] | H | CH3 | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | 13-F | |
 |
14-Hydroxy-LSD[24] | H | CH3 | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | 14-OH | |
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Jamieson CS, Misa J, Tang Y, Billingsley JM (2021-04-29). "Biosynthesis and synthetic biology of psychoactive natural products". Chemical Society Reviews. 50 (12): 6950–7008. doi:10.1039/D1CS00065A. ISSN 0306-0012. PMC 8217322. PMID 33908526.
“There are three main ergot alkaloid classes, clavines, ergoamides (lysergamides), and ergopeptides, with 3 belonging to the ergoamide class.” 2.5 Lysergic acid and LSD, p. 6970 - ^ Hofmann A (June 1959). "Psychotomimetic drugs; chemical and pharmacological aspects". Acta Physiologica et Pharmacologica Neerlandica. 8: 240–58. PMID 13852489.
- ^ US patent 2997470, Pioch RP, "LYSERGIC ACID AMIDES", published 1956-03-05, issued 1961-08-22
- ^ Hoffman AJ, Nichols DE (September 1985). "Synthesis and LSD-like discriminative stimulus properties in a series of N(6)-alkyl norlysergic acid N,N-diethylamide derivatives". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 28 (9): 1252–1255. doi:10.1021/jm00147a022. PMID 4032428.
- ^ Huang X, Marona-Lewicka D, Pfaff RC, Nichols DE (March 1994). "Drug discrimination and receptor binding studies of N-isopropyl lysergamide derivatives". Pharmacology, Biochemistry, and Behavior. 47 (3): 667–673. doi:10.1016/0091-3057(94)90172-4. PMID 8208787. S2CID 16490010.
- ^ Watts VJ, Lawler CP, Fox DR, Neve KA, Nichols DE, Mailman RB (April 1995). "LSD and structural analogs: pharmacological evaluation at D1 dopamine receptors". Psychopharmacology. 118 (4): 401–409. doi:10.1007/BF02245940. PMID 7568626. S2CID 21484356.
- ^ Nichols DE, Frescas S, Marona-Lewicka D, Kurrasch-Orbaugh DM (September 2002). "Lysergamides of isomeric 2,4-dimethylazetidines map the binding orientation of the diethylamide moiety in the potent hallucinogenic agent N,N-diethyllysergamide (LSD)". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 45 (19): 4344–4349. doi:10.1021/jm020153s. PMID 12213075.
- ^ Schiff PL (October 2006). "Ergot and its alkaloids". American Journal of Pharmaceutical Education. 70 (5): 98. doi:10.5688/aj700598 (inactive 2024-11-22). PMC 1637017. PMID 17149427.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: DOI inactive as of November 2024 (link) - ^ Passie T, Halpern JH, Stichtenoth DO, Emrich HM, Hintzen A (2008). "The pharmacology of lysergic acid diethylamide: a review". CNS Neuroscience & Therapeutics. 14 (4): 295–314. doi:10.1111/j.1755-5949.2008.00059.x. PMC 6494066. PMID 19040555.
- ^ Nichols DE (2017). "Chemistry and Structure-Activity Relationships of Psychedelics". Current Topics in Behavioral Neurosciences. 36: 1–43. doi:10.1007/7854_2017_475. ISBN 978-3-662-55878-2. PMID 28401524.
- ^ Brandt SD, Kavanagh PV, Westphal F, Stratford A, Elliott SP, Hoang K, et al. (September 2016). "Return of the lysergamides. Part I: Analytical and behavioural characterization of 1-propionyl-d-lysergic acid diethylamide (1P-LSD)". Drug Testing and Analysis. 8 (9): 891–902. doi:10.1002/dta.1884. PMC 4829483. PMID 26456305.
- ^ Brandt SD, Kavanagh PV, Westphal F, Elliott SP, Wallach J, Colestock T, et al. (January 2017). "Return of the lysergamides. Part II: Analytical and behavioural characterization of N6 -allyl-6-norlysergic acid diethylamide (AL-LAD) and (2'S,4'S)-lysergic acid 2,4-dimethylazetidide (LSZ)". Drug Testing and Analysis. 9 (1): 38–50. doi:10.1002/dta.1985. PMC 5411264. PMID 27265891.
- ^ Brandt SD, Kavanagh PV, Westphal F, Elliott SP, Wallach J, Stratford A, et al. (October 2017). "Return of the lysergamides. Part III: Analytical characterization of N6 -ethyl-6-norlysergic acid diethylamide (ETH-LAD) and 1-propionyl ETH-LAD (1P-ETH-LAD)". Drug Testing and Analysis. 9 (10): 1641–1649. doi:10.1002/dta.2196. PMC 6230477. PMID 28342178.
- ^ Brandt SD, Kavanagh PV, Twamley B, Westphal F, Elliott SP, Wallach J, et al. (February 2018). "Return of the lysergamides. Part IV: Analytical and pharmacological characterization of lysergic acid morpholide (LSM-775)". Drug Testing and Analysis. 10 (2): 310–322. doi:10.1002/dta.2222. PMC 6230476. PMID 28585392.
- ^ Brandt SD, Kavanagh PV, Westphal F, Stratford A, Elliott SP, Dowling G, et al. (August 2019). "Return of the lysergamides. Part V: Analytical and behavioural characterization of 1-butanoyl-d-lysergic acid diethylamide (1B-LSD)". Drug Testing and Analysis. 11 (8): 1122–1133. doi:10.1002/dta.2613. PMC 6899222. PMID 31083768.
- ^ Halberstadt AL, Klein LM, Chatha M, Valenzuela LB, Stratford A, Wallach J, et al. (February 2019). "Pharmacological characterization of the LSD analog N-ethyl-N-cyclopropyl lysergamide (ECPLA)". Psychopharmacology. 236 (2): 799–808. doi:10.1007/s00213-018-5055-9. PMC 6848745. PMID 30298278.
- ^ Kruegel AC. Novel Ergolines and Methods of Treating Mood Disorders. Patent WO 2022/226408
- ^ WO 2022/008627, Grill M, "Improved Method for the Production of Lysergic Acid Diethylamide (LSD) and Novel Derivatives thereof."
- ^ Brandt SD, Kavanagh PV, Gare S, Stratford A, Halberstadt AL. Analytical and behavioral characterization of 1-hexanoyl-LSD (1H-LSD). Drug Test Anal. 2024 Jul 4. doi:10.1002/dta.3767 PMID 38965834
- ^ Brandt SD, Kavanagh PV, Westphal F, Stratford A, Odland AU, Klein AK, et al. (June 2020). "Return of the lysergamides. Part VI: Analytical and behavioural characterization of 1-cyclopropanoyl-d-lysergic acid diethylamide (1CP-LSD)". Drug Testing and Analysis. 12 (6): 812–826. doi:10.1002/dta.2789. PMC 9191646. PMID 32180350.
- ^ Okada Y, Segawa H, Yamamuro T, Kuwayama K, Tsujikawa K, Kanamori T, et al. (June 2024). "Synthesis and analytical characterization of 1-(2-thienoyl)-6-allyl-nor-d-lysergic acid diethylamide (1T-AL-LAD)". Drug Testing and Analysis. doi:10.1002/dta.3747. PMID 38922764.
- ^ Usdin E, Efron DH. Psychotropic Drugs and Related Compounds. (1972) ASIN B002X3CDIY
- ^ WO 2021/076572, Olson DE, et al., "Ergoline-like compounds for promoting neural plasticity"
- ^ Libânio Osório Marta RF (August 2019). "Metabolism of lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD): an update". Drug Metabolism Reviews. 51 (3): 378–387. doi:10.1080/03602532.2019.1638931. PMID 31266388.
